|
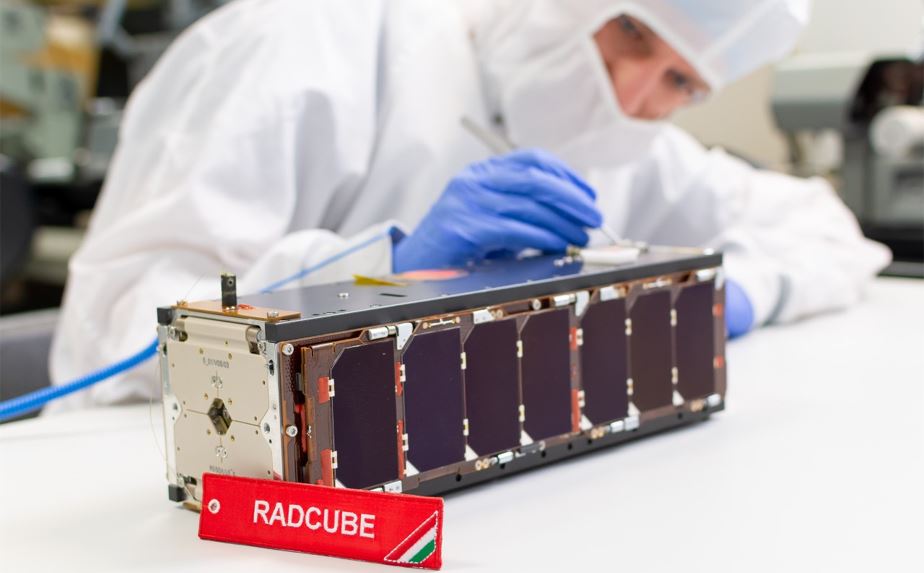
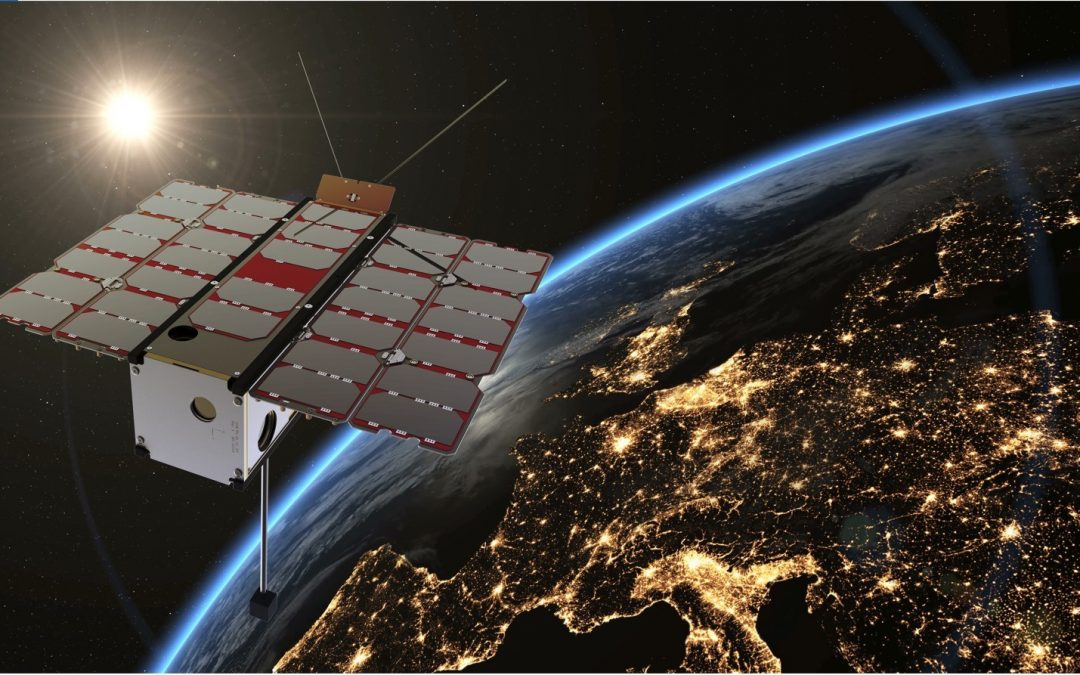
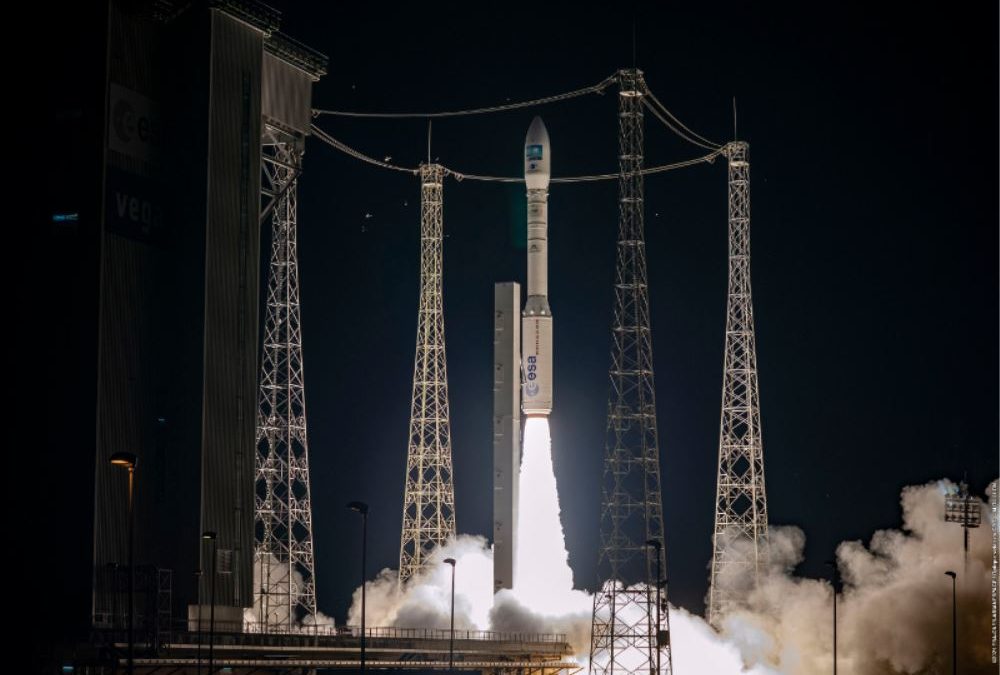
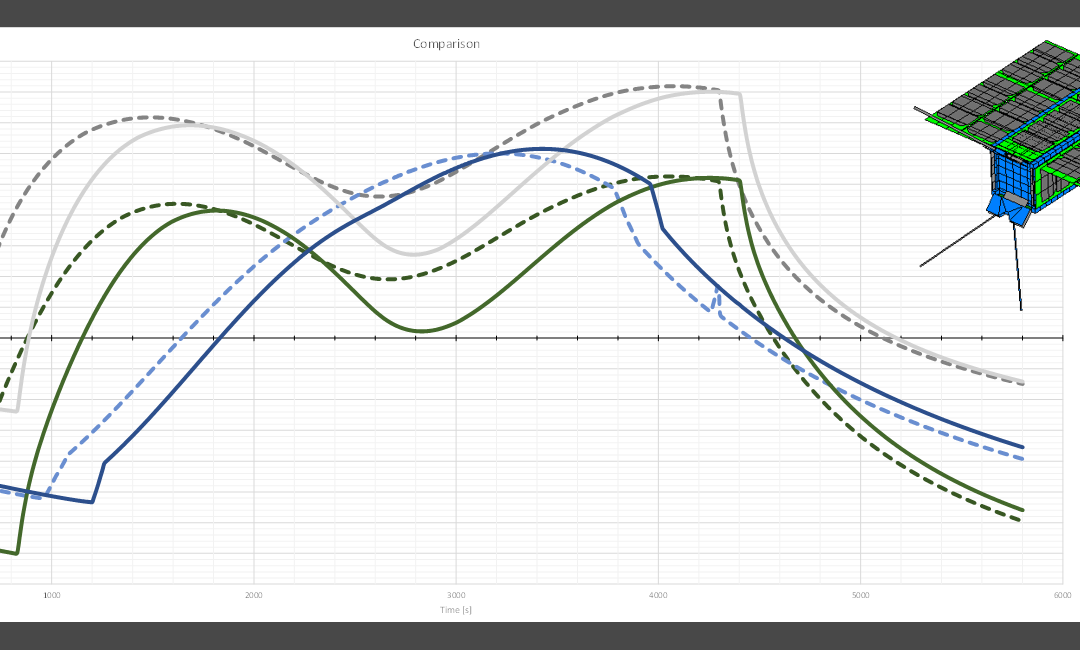
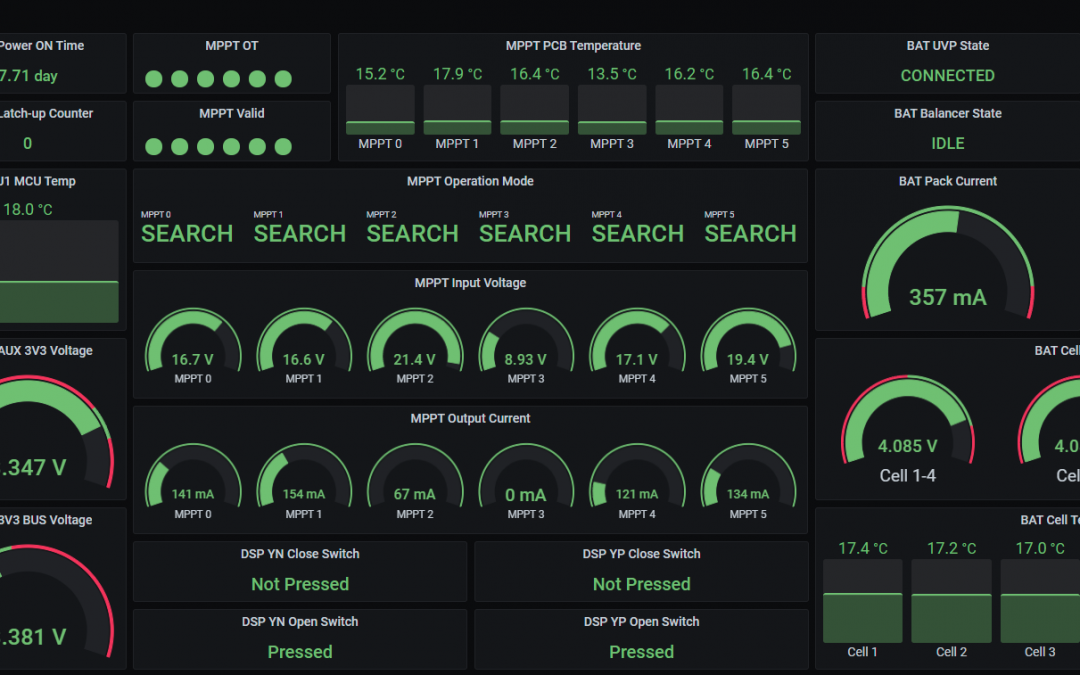
Because of global climate change, according to forecast the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, inland water events and droughts are going to increase in Hungary as well. The basis for measuring the current drought is soil moisture and vegetation condition. These reflect the rainfall and temperature conditions of the previous period. Traditionally, climate-based drought indices, calculated from station-based meteorological observations, have been used to characterize drought conditions throughout the world. Because these indices are based on ground-based point observations, as a result, climate-based drought index maps often depict broad-scale drought patterns that do not depict local-scale spatial variations in drought conditions. In contrast, according to the satellite data, the decision support system can estimate the amount of water in the topsoil at a higher resolution over a wider area, providing more accurate results for drought severity patterns. To monitor vegetation development, data is usually processed in the visible, near infrared and thermal infrared wavelengths, which provide spectral, spatially detailed and more localised information across the entire landscape. The importance of drought monitoring using satellite remote sensing begins when its data are used by farmers, decision-makers who rely on early warning information to improve management decisions. The Hungarian satellite project was launched as a response to the increased demand for digital agrometeorological data in Hungary, which is part of the Széchenyi Plan Plus. The small satellite, manufactured and operated after the launch by C3S Ltd., was implemented in cooperation with the members of the consortium led by COMBIT Computer Technology Ltd., the University of Óbuda and Széchenyi István University. The aim of the mission is to provide a forecast of areas at risk of drought during periods of increasingly frequent rainfall deficits, based on continuously updated data, to mitigate drought damage in Hungary through drought monitoring. Designed for a 3-year lifetime, the satellite will be launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California – currently scheduled for August.
Magyar műhold az aszályvédelemért A globális klímaváltozás következményeként az előrejelzések szerint hazánkban, illetve a régiónkban is fokozódni fognak a szélsőséges időjárási helyzetek, a belvizek és aszályok előfordulási gyakorisága, súlyossága. Ahhoz, hogy az aszály káros hatását enyhítsük vagy megelőzzük, ezek kialakulásának, fejlődésének megértése létfontosságú feladattá vált. Az aktuális aszály mérésének alapja, a talajnedvesség és a növényzet állapotának vizsgálata. Ezekben realizálódnak a megelőző időszak csapadék- és hőmérsékleti viszonyai. Hagyományosan az aszályos körülmények jellemzésére világszerte az állomásokon végzett meteorológiai megfigyelésekből számított, éghajlati alapú aszályindexeket használnak. Mivel ezek az indexek földi pontmegfigyeléseken alapulnak, gyakran olyan széles skálájú aszálymintákat ábrázolnak, amelyek nem mutatják az aszályos körülmények helyi szintű térbeli változásait. Ezzel szemben a műhold adatai alapján a döntéstámogató rendszer a talaj felső rétegében lévő vízmennyiséget nagyobb felbontásban, szélesebb területen tudja megbecsülni, ezzel pontosabb eredményt szolgáltat az aszály súlyossági mintáira vonatkozóan. A növényzet fejlődésének megfigyeléséhez, általában a látható, a közeli infravörös és a termál infravörös hullámhosszban gyűjtött adatokat dolgozzák fel, mely a teljes tájra kiterjedő, részletes felszíni felbontás megfigyelését biztosítják. A műholdas távérzékeléssel történő aszálymegfigyelés jelentősége ott kezdődik, amikor adatait a mezőgazdasági termelők, a korai figyelmeztető információkra támaszkodó döntéshozók a gazdálkodási döntések javítására használják fel. Hazánkban a digitális agrometeorológiai adatszolgáltatásra megnőtt igény miatt indult el a magyar műhold projekt, mely a Széchenyi Terv Plusz része. A C3S Kft. által gyártott és a felbocsátást követően üzemeltetett kisműholdja, a COMBIT Számítástechnikai Zrt. által vezetett konzorcium tagjaival az Óbudai Egyetem és a Széchenyi István Egyetem együttműködésében valósult meg. A WREN-1 (Water Resources in Efficient Networks) a 6U méretű nanoműhold, pályára állítása után rendszeres távérzékelt adatokat fog továbbítani Magyarország területéről. A küldetés célja az, hogy a folyamatosan frissülő adatok ismeretében, az egyre gyakrabban előforduló csapadékhiányos időszakokban előrejelzést adjon az aszállyal veszélyeztetett területekről, ezzel az aszálymonitoringnak köszönhetően mérsékelhetővé tegye hazánkban az aszálykárokat. A 3 éves élettartamra tervezett műhold felbocsátása a kaliforniai Vandenberg Űrbázisról indul majd – a jelenlegi tervek szerint augusztusban.
|

C3S at Space Tech Expo 2022
Good morning Bremen! As returning exhibitors, it is amazing to see the evolution of Space Tech Expo Europe and the whole industry year by year. We are happy to be here again, share our new experiences, introduce our new products and prospects, and meet inspiring...